为自己模拟的IOC容器添加上DI注入
一、介绍
上一篇中,模拟Spring实现了一个简易的IOC容器,完成了初始化bean的操作,统一交给了一个Map集合进行管理。
模拟Spring实现一个简易的IOC容器
现在,将为这个IOC容器添加DI注入功能
二、实现
在编写之前,我们先加一个工具类,用来获取接口所实现的子类Class对象,也是通过子类
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>org.reflections</groupId>
<artifactId>reflections</artifactId>
<version>0.10.2</version>
</dependency>
|
代码如下,对比上一次,稍稍做了一点封装,使得步骤更加清晰
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| package com.banmoon.test.mockioc.annotation;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface Di {
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
189
190
| package com.banmoon.test.mockioc.core;
import cn.hutool.core.collection.CollUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.util.ArrayUtil;
import cn.hutool.core.util.StrUtil;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.annotation.Bean;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.annotation.Di;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.reflections.Reflections;
import java.io.File;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.net.URLDecoder;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Objects;
import java.util.Set;
@Slf4j
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class MyApplicationContext {
private static final Map<String, Object> singleObjects = new HashMap<>();
private static String currentAbsPath = null;
private String packagePath;
private Reflections packageReflections;
public MyApplicationContext(String packagePath) throws Exception {
this.packagePath = packagePath;
this.packageReflections = new Reflections(packagePath);
String basePackage = StrUtil.replace(packagePath, ".", "\\");
URL url = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader().getResource(basePackage);
if (Objects.nonNull(url)) {
String filePath = URLDecoder.decode(url.getFile(), "utf-8");
currentAbsPath = filePath.substring(0, filePath.length() - basePackage.length());
scanBean(new File(filePath));
}
}
private void scanBean(File file) throws ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
if (file.isDirectory()) {
File[] children = file.listFiles();
if (ArrayUtil.isEmpty(children)) {
return;
}
for (File child : children) {
if (child.isDirectory()) {
scanBean(child);
} else {
String pathWithClass = child.getAbsolutePath().substring(currentAbsPath.length() - 1);
if (pathWithClass.endsWith(".class")) {
String classPath = StrUtil.replace(pathWithClass, "\\", ".")
.replace(".class", "");
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(classPath);
initializeBean(clazz, false);
}
}
}
}
}
public <T> T getBean(String beanName, Class<T> clazz) {
Object o = singleObjects.get(beanName);
if (!clazz.isInstance(o)) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("获取的类型错误");
}
return (T) o;
}
private String generateBeanName(Bean annotation, Class<?> clazz) {
String value = annotation.value();
if (StrUtil.isBlank(value)) {
Class<?>[] interfaces = clazz.getInterfaces();
if (ArrayUtil.isNotEmpty(interfaces)) {
value = StrUtil.lowerFirst(interfaces[0].getSimpleName());
} else {
value = StrUtil.lowerFirst(clazz.getSimpleName());
}
}
return value;
}
private void diField(Object currentObj, Class<?> clazz) {
Field[] fields = clazz.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
Di annotation = field.getAnnotation(Di.class);
if (Objects.nonNull(annotation)) {
Class<?> fieldClazz = field.getType();
Object o = initializeBean(fieldClazz, true);
try {
field.set(currentObj, o);
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
log.error("DI注入异常", e);
}
}
}
}
public Object initializeBean(Class<?> clazz, boolean find) {
if (clazz.isInterface() && find) {
Set<Class<?>> set = packageReflections.getSubTypesOf((Class<Object>) clazz);
clazz = CollUtil.get(set, 0);
} else if (clazz.isInterface() && !find) {
return null;
}
Bean beanAnnotation = clazz.getAnnotation(Bean.class);
if (Objects.isNull(beanAnnotation)) {
return null;
}
try {
String beanName = generateBeanName(beanAnnotation, clazz);
Object o = null;
if (find) {
o = singleObjects.get(beanName);
}
if (Objects.isNull(o)) {
Constructor<?> constructor = clazz.getConstructor();
Object obj = constructor.newInstance();
singleObjects.put(beanName, obj);
diField(obj, clazz);
}
return o;
} catch (Exception exception) {
log.error("初始化bean异常", exception);
return null;
}
}
}
|
三、测试
同样,service及其实现类,dao及其实现类
1
2
3
4
5
6
| package com.banmoon.test.mockioc.service;
public interface TestService {
void hello();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
| package com.banmoon.test.mockioc.service.impl;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.annotation.Bean;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.annotation.Di;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.dao.TestDao;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.service.TestService;
@Bean
public class TestServiceImpl implements TestService {
@Di
public TestDao testDao;
@Override
public void hello() {
System.out.println("service hello...");
testDao.hello();
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
| package com.banmoon.test.mockioc.dao;
public interface TestDao {
void hello();
}
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| package com.banmoon.test.mockioc.dao.impl;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.annotation.Bean;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.dao.TestDao;
@Bean
public class TestDaoImpl implements TestDao {
@Override
public void hello() {
System.out.println("dao hello...");
}
}
|
在service实现类上面有dao类型的属性,并加上了@Di注解,试试能不能成功注入
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
| package com.banmoon.test.mockioc;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.core.MyApplicationContext;
import com.banmoon.test.mockioc.service.TestService;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MyApplicationContext context = new MyApplicationContext("com.banmoon.test.mockioc");
TestService testService = context.getBean("testService", TestService.class);
testService.hello();
}
}
|
运行查看结果,成功
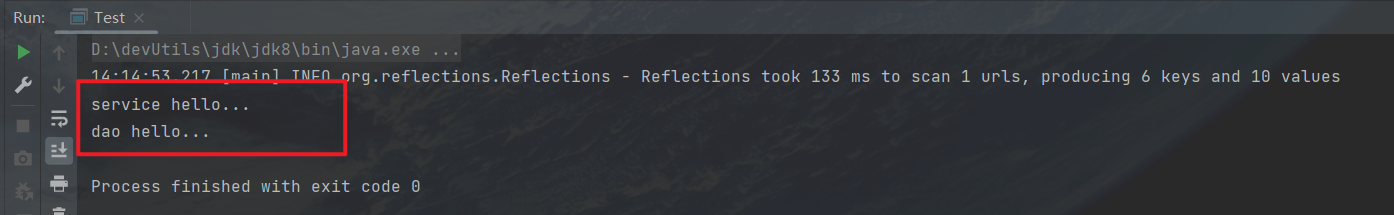
四、最后
其实,这也是最为简单的注入,我就问问
都说Spring使用了三级缓存,那么这三级缓存是怎么使用的,它有什么作用呢?
我是半月,你我一同共勉!!!











